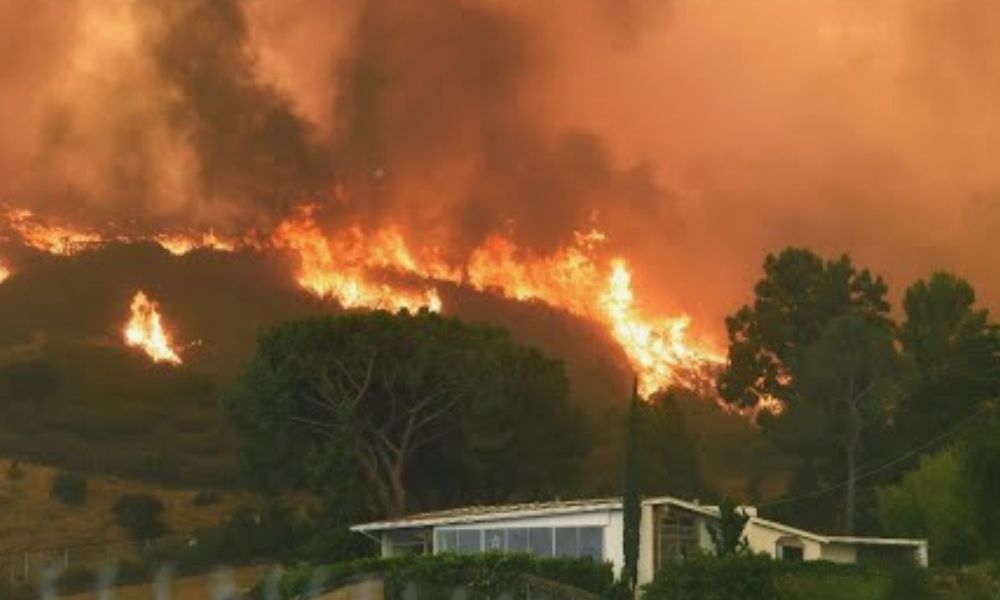

Understanding the Impact: A Comprehensive Guide to Los Angeles-Area Fires
The threat of wildfires is a growing concern for many areas across California, but the Los Angeles region, with its mix of urban sprawl, rugged terrain, and dry climate, is particularly vulnerable. Over the years, Los Angeles-area fires have become more frequent and intense, with devastating consequences for both residents and the environment. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the factors that contribute to these fires, their impact on the community, and how individuals and local authorities can prepare for and mitigate their effects.
The Growing Threat of Fires in the Los Angeles Area
Los Angeles County is no stranger to wildfires, with its hot, dry summers, Santa Ana winds, and vast expanses of vegetation, all contributing to the ideal conditions for fires to ignite and spread rapidly. Over the last few decades, the frequency, intensity, and scale of these fires have increased, largely due to climate change, land management practices, and population growth in fire-prone areas.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and shifting weather patterns have created more favorable conditions for fires to start and spread. Dry vegetation, combined with stronger winds, allows fires to move quickly across both urban and wildland areas.
- Urban-Wildland Interface: Los Angeles is home to both densely populated neighborhoods and expansive wilderness areas. As development continues to encroach on fire-prone regions, the risk of fires impacting communities grows, creating a dangerous “urban-wildland interface” where fires can easily threaten homes and infrastructure.
- Fire Seasonality: While fires can occur at any time of year, the peak of the fire season in Southern California typically runs from late summer into fall. The months of August through November tend to bring the most severe fires due to high temperatures, dry vegetation, and the presence of the Santa Ana winds, which can gust up to 60 miles per hour, fanning the flames.
The Economic and Environmental Impact of Fires
The effects of Los Angeles-Area Fires are extend far beyond the immediate danger to life and property. They also cause significant economic and environmental damage, with long-lasting repercussions for both the local community and the region as a whole.
1. Damage to Property and Infrastructure
Each year, wildfires in the Los Angeles-Area Fires region destroy hundreds of homes and businesses, particularly in the hills and mountainous areas where residential communities are located close to wilderness. In addition to the physical destruction, fires can lead to significant economic losses, as recovery and rebuilding efforts can take years and cost billions of dollars.
2. Impact on the Environment
Fires contribute to the destruction of vital ecosystems, particularly in areas like the Angeles National Forest, where native plants and wildlife are severely impacted. Many species that rely on these habitats face loss of shelter and food sources, and the environmental damage can take decades to fully recover. The soil in fire-affected areas can also become more vulnerable to erosion, leading to issues with water quality and increased risk of landslides, particularly after rains.
3. Air Quality and Health Effects
Smoke from wildfires can travel hundreds of miles, affecting air quality far beyond the immediate fire zone. In the Los Angeles-Area Fires, smoke can contribute to unhealthy levels of particulate matter in the air, exacerbating respiratory problems, particularly for children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing conditions such as asthma or heart disease. Long-term exposure to wildfire smoke can have serious health consequences, including respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
4. Economic Disruption
Los Angeles-Area Fires not only damage homes and infrastructure but can also disrupt local businesses and the regional economy. Tourism, which plays a significant role in Southern California’s economy, can take a hit due to air quality concerns or the destruction of popular outdoor attractions. Additionally, the cost of firefighting efforts, evacuation procedures, and recovery can put a strain on local government resources.
The Role of Firefighting and Preparedness
Local authorities, residents, and emergency responders play crucial roles in preventing and mitigating the effects in the Los Angeles-Area Fires. Here are a few key factors in fire management and preparedness:
1. Firefighting Strategies
The Los Angeles-Area Fires Department (LAFD) and other local agencies are equipped with specialized tools and strategies for combating wildfires. Air tankers, helicopters, and ground crews work together to control fires, but the rapidly changing nature of these fires, especially during high winds, can make suppression efforts extremely challenging. Firebreaks—gaps in vegetation designed to stop the spread of fire—are often used to protect communities, but they can only do so much.
2. Evacuation and Communication
Clear communication is essential for keeping residents safe during a fire. Authorities issue evacuation orders to ensure that people in fire-affected areas are able to leave quickly and safely. However, evacuation efforts can be complicated by heavy smoke, high winds, and the speed at which fires spread, necessitating efficient alert systems like emergency notifications and public service announcements.
3. Preparedness for Residents
For residents in fire-prone areas, preparedness is key. Many of the worst impacts of fires can be mitigated with proactive steps, such as:
Creating defensible space around homes by clearing dead vegetation and using fire-resistant building materials
Having an evacuation plan in place and ensuring all family members are familiar with it
Installing fire-resistant roofs and windows to protect against flying embers
Staying informed through local authorities and emergency services about potential fire threats
4. Community Resilience and Recovery
Post-fire recovery can take years, particularly for those who lose their homes. Community support networks, government assistance, and rebuilding efforts are crucial in helping those affected recover. Local organizations and authorities often provide temporary housing, food, and financial support to fire survivors, but long-term recovery requires significant investment and coordination.
The Future of Los Angeles-Area Fires
As climate change continues to alter weather patterns, the frequency and severity of Los Angeles-Area Fires are expected to increase. This presents a growing challenge for local authorities, communities, and emergency responders, who must continually adapt to the changing landscape of fire risks.
However, there are opportunities for improvement through the implementation of better fire prevention strategies, such as controlled burns, improved land management practices, and enhanced building codes that prioritize fire resistance. Public education campaigns aimed at raising awareness about fire risks and preparedness are also essential in helping residents protect themselves and their homes.
Conclusion
The wildfires that impact the Los Angeles area are a powerful reminder of the destructive force of nature and the growing challenges posed by climate change. Understanding the factors that contribute to these fires, their broad economic and environmental consequences, and the role of fire prevention and preparedness is essential for minimizing their impact.
By working together—individuals, communities, and local authorities—Los Angeles can better prepare for the increasing threat of wildfires and ensure the safety and resilience of its residents in the face of an unpredictable future.









Post Comment